On our Instagram page, we posted a carousel explaining what is the difference between Audio Gain vs Volume. But a carousel is a group of not more than 5 posts and it couldn’t justify giving the answer properly and in detail.

CREATE MIX YOU CAN FEEL PROUD OF
If You Want To Mix Your Music Like Professionals,
You Have To Learn From Professionals And We Have Made It EASY For You.
So, here we are… In this blog, you are going to learn about the Gain vs Volume in complete detail.
Many people think that both – Gain and Volume are one and the same thing. But that’s not. There is a huge difference between Gain vs Volume in terms of many factors. You will get to know about some practical as well as technical differences between gain and volume here.
Mixing audio is a crucial step in the music production process. It involves combining multiple audio tracks into a single, cohesive mix that sounds great and is ready for mastering. One of the key concepts in mixing is the difference between gain and volume. Although they are often used interchangeably, they have different purposes and it’s essential to understand the difference between the two. In this blog, we will take a closer look at gain vs volume in mixing and how they impact the sound of your mix.
So without boring you further, let’s dive into the topic. But first, let’s see the 5 key differences between Gain vs Volume.
Also Read: What is Compressor Ratio?
Contents
5 Key Difference between Gain vs Volume
| GAIN | VOLUME |
|---|---|
| Gain is Input of the Audio System | Volume is the Output of the Audio system |
| The Gain controls loudness before processing. | The Volume controls loudness after processing. |
| The Gain turns up the Input Signal. | The volume turns up the Output Signal |
| Gain is a function of current | Volume is the function of Voltage |
| If the Gain is changed, the tone and quality of the sound change too. | If the Volume is changed, the tone and quality of the sound remain the same. |
What is Gain in Audio and on AMP
If you’ve bought your new Guitar, or an audio interface, or the channel strips(real or digital), then definitely you must have come across the word – “GAIN” many a time. And this may have brought too many questions into your head.
So let’s get the answer to the question – what is Gain on a guitar amplifier and on other audio instruments?
Gain is the term used to describe the amount of amplification applied to a sound source. Gain is measured in decibels (dB) and it is the first stage of processing in the mixing process. Gain is used to increase or decrease the level of the sound source so that it can be correctly balanced with the other sounds in the mix.
Gain is applied to individual tracks, such as drums, bass, guitar, and vocals, and it is used to set the right level for each track. This level is important because it affects the overall balance of the mix and it is essential to get this right before moving on to the next stage of mixing.
We have the basic perception about the Gain that generally by turning up, the volume gets increased automatically. But how is gain different from volume?
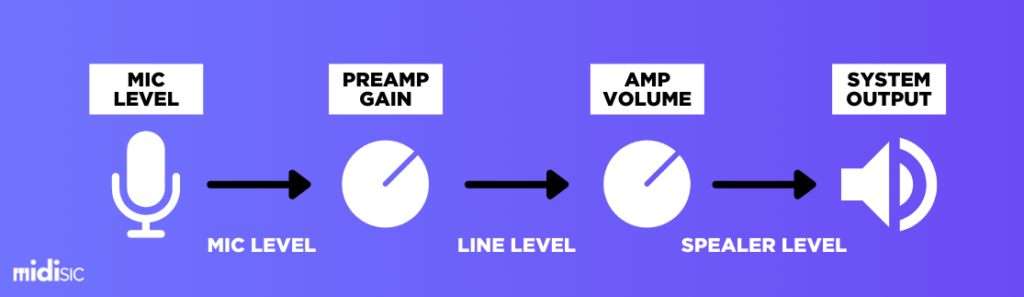
Well let me tell you, Gain is a little complicated to understand in comparison to the volume. Gain is related to the change that takes place in the input stage before the processing. A ‘TRIM’ control or a Microphone preamp’s gain control works in turning up the microphone’s input signal to a recordable level.
Whereas on the Guitar amplifier, ‘Drive’ or Gain control usually controls the level of signals hitting the preamp stage. Although Gain does increase the volume, that is just fundamentally a different topic.
In the olden days, when the time of analog systems, gain was considered a very simple concept. But, as we moved to this digital era, the meaning of word ‘Gain’ has emerged to have several meanings.
Sometimes, the gain is considered to be just another name for the volume. You get to see that very commonly on digital plugins. If we take an example, the ‘Makeup Gain’ function on a compressor is just the output volume with another name.
Also Read: Types of Audio Compressor
Basically, if we define gain through our own words, it’ll be – The gain control defines the loudness of something before that goes to any processing. It’s a volume level that is sent into your plugins, preamps, as well as to amplifiers.
So if we take an overall discussion, we can summarise gain in three things:
- An alternate word for the Volume, or understanding the level of loudness.
- The level of loudness of Input.
- Distortion
Remember when you’re mixing, you’d probably see all three factors given above.
Additional Details: ‘Gain’ is also referred to as ‘distortion’.
Why is Gain Important?
Gain is important because it allows you to control the levels of the different sound sources in your mix. This helps you to avoid clipping and distortion, which can be very noticeable and detract from the overall quality of your mix. Clipping occurs when the audio level is too high, causing the waveform to clip off and produce an unpleasant, harsh sound.
By setting the gain correctly, you can ensure that each track is at the correct level, which will make the mix easier to control and allow you to apply processing and effects to each track with greater precision.
How is Gain Measured?
The Gain or say input volume of any system is measured in decibels. The decibel is addressed in the short form of dB.
Gain is typically measured in decibels (dB). A gain of 0 dB means that the output level of the system is equal to the input level, and a gain greater than 0 dB indicates that the output level is higher than the input level.
A gain of less than 0 dB means that the output level is lower than the input level. For example, a gain of +6 dB means that the output level is double the input level, while a gain of -6 dB means that the output level is half the input level.

CREATE MIX YOU CAN FEEL PROUD OF
If You Want To Mix Your Music Like Professionals,
You Have To Learn From Professionals And We Have Made It EASY For You.
What is Gain on the Guitar Amp?
The “Gain” control on a guitar amplifier is used to increase or decrease the volume of the input signal from the guitar, which allows the player to fine-tune the output level and create different distortion or saturation effects.
Again, the Gain on the guitar amp is the same as the normal gain. As I already explained above, Gain is related to the change that takes place in the input stage before the processing. A ‘TRIM’ control or a Microphone preamp’s gain control works in turning up the microphone’s input signal to a recordable level.
If you increase or decrease gain, the quality of sound changes accordingly. So basically I want to tell you here that understanding the gain is very important, as it controls the tone of the song/track and not the loudness.
What is Gain Staging?
The word “Gain Staging” is yet another word that is thrown a lot in the music producers’ world. So What does Gain Staging mean?
Also Read: What is Frequency Response in Microphone?
Gain staging refers to the process of setting the gain levels of individual components in a sound system or recording chain to optimize the signal level and minimize noise and distortion. This involves setting the gain level of each component, such as microphone preamps, equalization, compressors, and amplifiers so that the signal remains at an optimal level throughout the entire signal chain.
The goal of gain staging is to ensure that the signal is not overloaded or under-utilized and that there is enough headroom to allow for processing without causing clipping or other distortions. Proper gain staging is an important aspect of achieving high-quality sound in professional audio recording and sound reinforcement systems.
If we ask Wikipedia it says, The Ideal gain staging occurs when each component in an audio signal flow is receiving and transmitting a signal in the optimum region of its dynamic range.
What is Volume in Gain vs Volume
Now we came to the Volume part. As I explained how the gain is reserved for the input level on a source, the Volume after processing works on the output level of a signal. The Volume is usually measured in dB SPL and can be generally measured down by the loudness that we hear.
When you mix in your DAW, each track on that DAW is routed to a master stereo channel or to the mix bus, if you have created one. Using the example of the real world, you can call, how loud the output of the master is, “Volume”. If we take a simple real example, When you turn up the volume knob in your car, the volume of the stereo increases.
A Volume knob is something that controls the sound range coming from the system. The system could be anything like your headphones, monitors, or car speakers. So basically, a ‘System’ in this case could be anything that produces sound.
How is Volume Measured?
As I said above, the volume is measured in decibels. The decibel is basically written in the short form – dB. So the higher the decibel, the louder the sound, and the lower the dB, the lesser the sound you will hear.
Let’s take some simple references on the decibels of some of the systems:
- Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs): The reference level in most DAWs is typically set at -18 dBFS (decibels relative to full scale). This means that 0 dBFS is the maximum level that a digital system can handle without distortion.
- Professional audio systems: In professional audio systems, the reference level is often set at +4 dBu. This is a professional audio level that is commonly used in studios and live sound reinforcement systems.
- Headphone levels: The recommended headphone level is around 85 dB SPL (sound pressure level). This is the level at which most people can listen to headphones for an extended period of time without damaging their hearing.
- Live music concerts: Live music concerts can reach decibel levels as high as 115 dB SPL. This is considered the maximum safe exposure level for hearing, and anything above this level can cause permanent hearing damage.
- Normal conversation: Normal conversation is usually around 60-70 dB SPL.
- Home theaters: The recommended reference level for home theaters is around 75 dB SPL.
These are just a few common reference levels for different systems, and it’s important to note that actual decibel levels can vary depending on the specific system and the sound source. However, understanding decibel levels can help you make informed decisions about the relative loudness of different systems and can help you achieve the desired results in your audio mixing and mastering
Why is Volume important?
Volume is important because it affects the overall loudness of the mix. The volume level should be set correctly because it affects the way your mix sounds when played back on different playback systems. A mix that is too quiet will not be audible on a loud sound system, while a mix that is too loud may cause distortion and affect the quality of the sound.
In addition, the volume level affects the perceived loudness of the mix. A mix that is too quiet may not have enough impact, while a mix that is too loud may be fatiguing to listen to. It’s important to find the right balance between loudness and clarity in your mix.
What is the Volume in a Guitar Amp?
As you’ve learned above, the volume in the guitar amp is something that you can control using the nobs that are given by the system.
Controlling the volume knobs or volume of the track doesn’t mean you are controlling anything related to the tone or texture of that same track. No matter how loud or low your volume is, the quality of the song will remain the same.
Gain vs Volume in Mixing: The Differences

CREATE MIX YOU CAN FEEL PROUD OF
If You Want To Mix Your Music Like Professionals,
You Have To Learn From Professionals And We Have Made It EASY For You.
For the musicians who really wish to enter some interesting territory, you may discover how loudness is admittedly subjective in acoustics and also about our sense of volume that varies at differing frequencies.
In order to get everything, you are required to understand the distinction completely as far as the gain and volume go.
We now know that earlier thinking about the gain and volume as the same was a mistake. Although gain and volume may be used sometimes reciprocally, they have differences that are technical and are extremely important to understand if you want to get the right mix.
How are Gain and Volume Different?
Let’s understand this in short:
- Gain generally controls something that comes into a piece of gear.
- The Volume usually controls something that comes out of a piece of gear.
Conclusion: Gain vs Volume
We’ve reached the final showdown of the gain vs volume. Till now, I hope you must have cleared the doubt for which you came here. So in the final, I’ll tell you the main point to remember to understand the key difference between the gain and volume.
Gain and volume are two different concepts in mixing, but they are often used interchangeably. However, it’s important to understand the difference between the two and how they impact the sound of your mix.
Gain is used to control the levels of the individual sound sources, while volume is used to control the final output level of the mix. Gain is applied at the start of the mixing process and it affects the overall balance of the mix, while volume is applied at the end of the mixing process and it affects the overall loudness of the mix.
Another important difference between gain and volume is that gain affects the dynamic range of the mix, while volume does not. Dynamic range is the difference between the loudest and quietest parts of a mix
Final Recap…
- The Gain is something that tells you how loud the INPUT of the channel or amp is. The gain controls the texture and the quality of the sound and not the loudness.
- The Volume is the one that controls how loud the OUTPUT of the channel or amp will be. It has the control over loudness of the track and not the tone.
FAQ
To let you know again, Volume is control over the output signals and the loudness of a sound system. It doesn’t affect the quality of the sound. Whereas the Gain lets you increase the loudness from the inside of an audio system. Now the gain can control the quality of the sound.
So, the answer to the question is No, Gain does not increase Volume.
If you set your gain too low, your amplifier won’t be able to reach full power. This will cause clipping from the source unit which will result in causing a distorted signal delivered to your speakers.
The above condition is relevant with the low voltage sources that are lower than 2.5 Volts.
Gain is the amplification factor. It’s generally the ratio of output over input. You’ll get more overdrive/distortion as you’ll turn the gain knob up, Basically, Distortion can be called the more extreme version of overdrive.
When choosing the right volume, the most common mistake that people do is to crank the subwoofer’s volume dial to its maximum setting. And that cause problem. In order to get rid of that mistake, you are required to choose the correct volume level.
So the ideal volume dial to set the subwoofer is around 75%.
The gain control helps to tune up the amp’s input stage in order to accept the head unit’s voltage level.
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to the question of whether volume or gain is better. Both volume and gain have different purposes in the audio mixing process, and they both have an impact on the sound of your mix. The choice between volume and gain will depend on the specific needs of your mix and the results you are trying to achieve.
Gain is used to control the levels of individual sound sources and set the balance of the mix, while volume is used to control the overall loudness of the mix. If you are having trouble balancing the levels of your sound sources, you may need to adjust the gain to ensure that each track is at the correct level. If you are having trouble with the overall loudness of your mix, you may need to adjust the volume.
In general, it’s recommended to start by setting the gain correctly, as this will help to avoid clipping and distortion. Once the gain is set, you can then adjust the volume to achieve the desired loudness level.
Ultimately, the choice between volume and gain will depend on the specific needs of your mix and the results you are trying to achieve. It’s important to understand the difference between the two and how they impact the sound of your mix, so you can make informed decisions and achieve the desired results.
Yes, the gain can affect volume. Gain is a control that adjusts the level of an audio signal before it is sent to the mixing console’s volume control. Gain increases or decreases the amplitude of an audio signal, which directly affects its volume. If the gain is set too high, it can cause the audio signal to become distorted or clipped, resulting in an undesirable sound. On the other hand, if the gain is set too low, the audio signal may become too quiet, making it difficult to hear in the mix.
In general, the gain control should be used to set the levels of individual tracks or sound sources, while the volume control should be used to adjust the overall loudness of the mix. By setting the gain correctly, you can avoid clipping and distortion, and then use the volume control to adjust the overall loudness of the mix to your liking.
In summary, gain and volume are closely related, and both have an impact on the volume of an audio signal. However, they serve different purposes in the audio mixing process, and it’s important to understand the difference between the two and how they impact the sound of your mix.
The ideal setting for gain depends on the specific needs of your audio mix and the desired results. In general, it’s recommended to set the gain at a level that provides enough signal strength to avoid distortion, while also providing enough headroom to allow for further processing and mixing.
If the gain is set too high, it can cause the audio signal to become clipped or distorted, resulting in an undesirable sound. On the other hand, if the gain is set too low, the audio signal may become too quiet and difficult to hear in the mix.
The best way to determine the ideal gain setting is to monitor the levels of your audio signal while adjusting the gain. You should aim to set the gain so that the audio signal is as strong as possible without reaching the point of distortion or clipping. This will depend on the specific equipment you are using and the sound sources you are working with, so it’s important to be aware of the levels and adjust the gain accordingly.
In summary, the ideal gain setting will depend on the specific needs of your mix and the desired results. A good starting point is to set the gain so that the audio signal is strong enough to avoid distortion and clipping while providing enough headroom for further processing and mixing.

CREATE MIX YOU CAN FEEL PROUD OF
If You Want To Mix Your Music Like Professionals,
You Have To Learn From Professionals And We Have Made It EASY For You.


 Over 250+ Pages of Mixing Guide
Over 250+ Pages of Mixing Guide
